Where possible, we recommend using the Apache Cassandra native capability to migrate data from your existing cluster into Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra by configuring a hybrid cluster. This capability uses Apache Cassandra's gossip protocol to replicate data from your source datacenter into your new managed-instance datacenter in a seamless way. However, there might be some scenarios where your source database version is not compatible, or a hybrid cluster setup is otherwise not feasible.
This tutorial describes how to migrate data to Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra in a live fashion by using a dual-write proxy and Apache Spark. The dual-write proxy is used to capture live changes, while historical data is copied in bulk using Apache Spark. The benefits of this approach are:
- Minimal application changes. The proxy can accept connections from your application code with few or no configuration changes. It will route all requests to your source database and asynchronously route writes to a secondary target.
- Client wire protocol dependency. Because this approach is not dependent on back-end resources or internal protocols, it can be used with any source or target Cassandra system that implements the Apache Cassandra wire protocol.
The following image illustrates the approach.
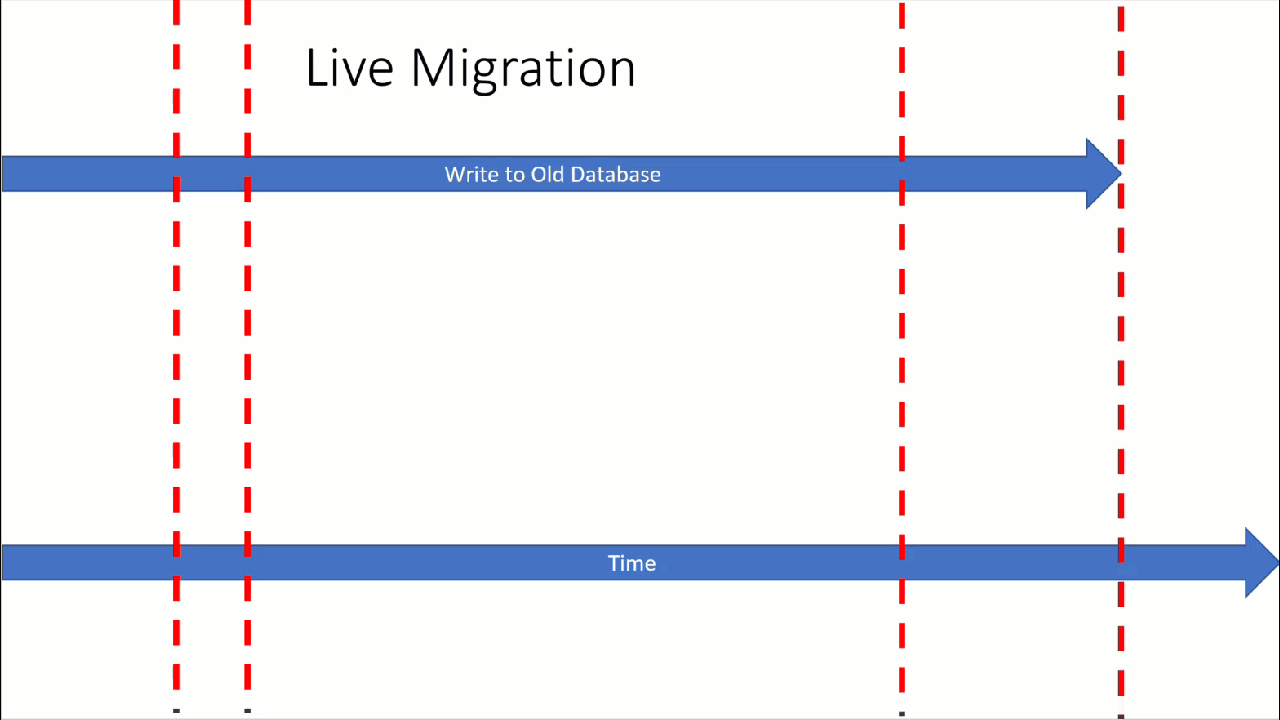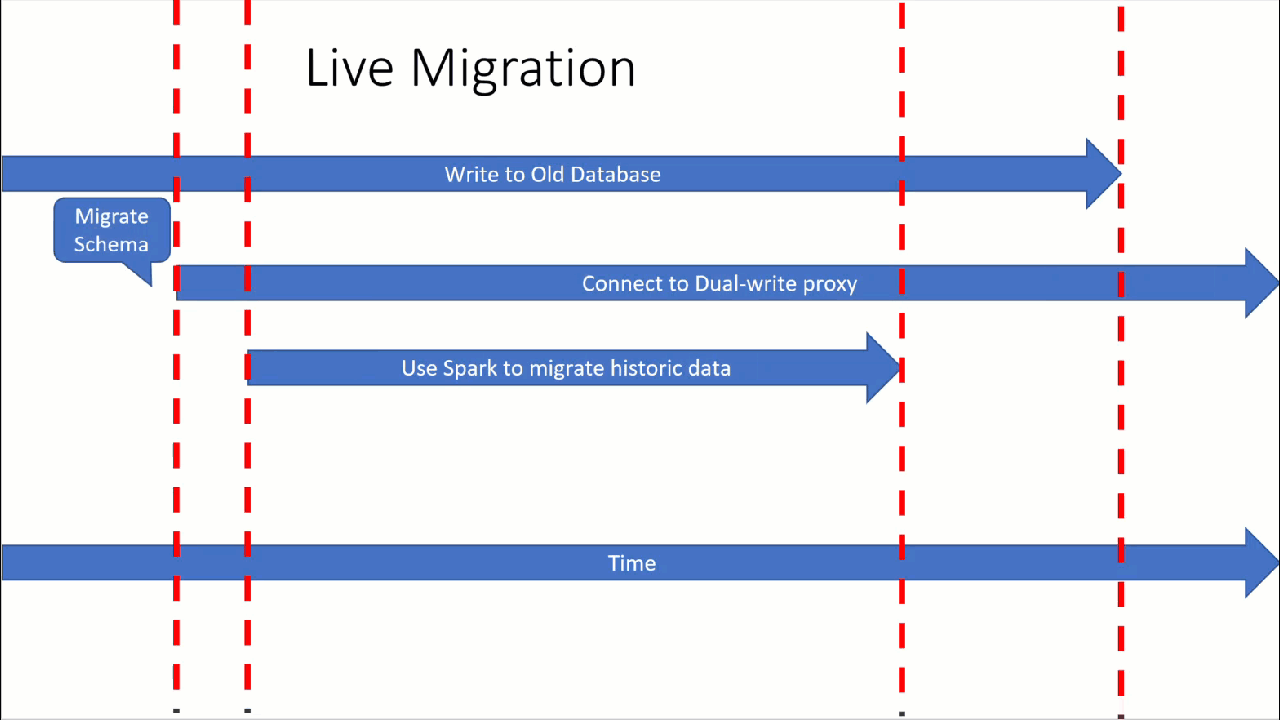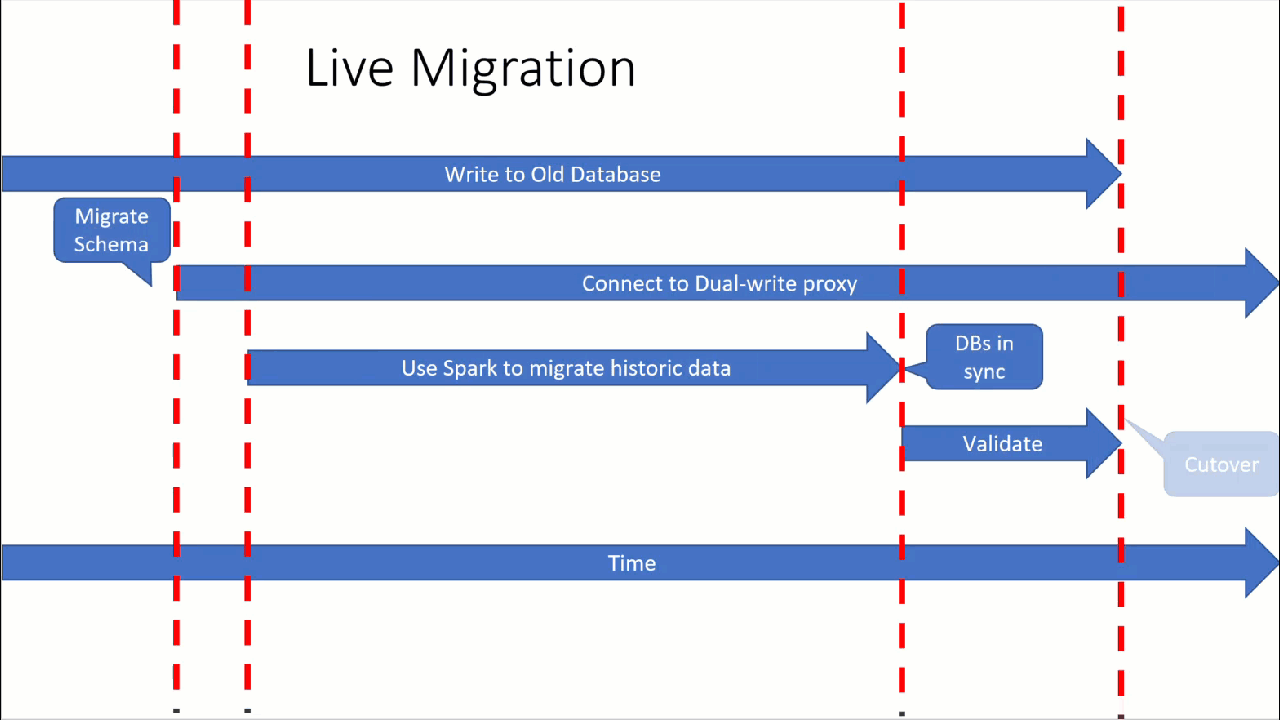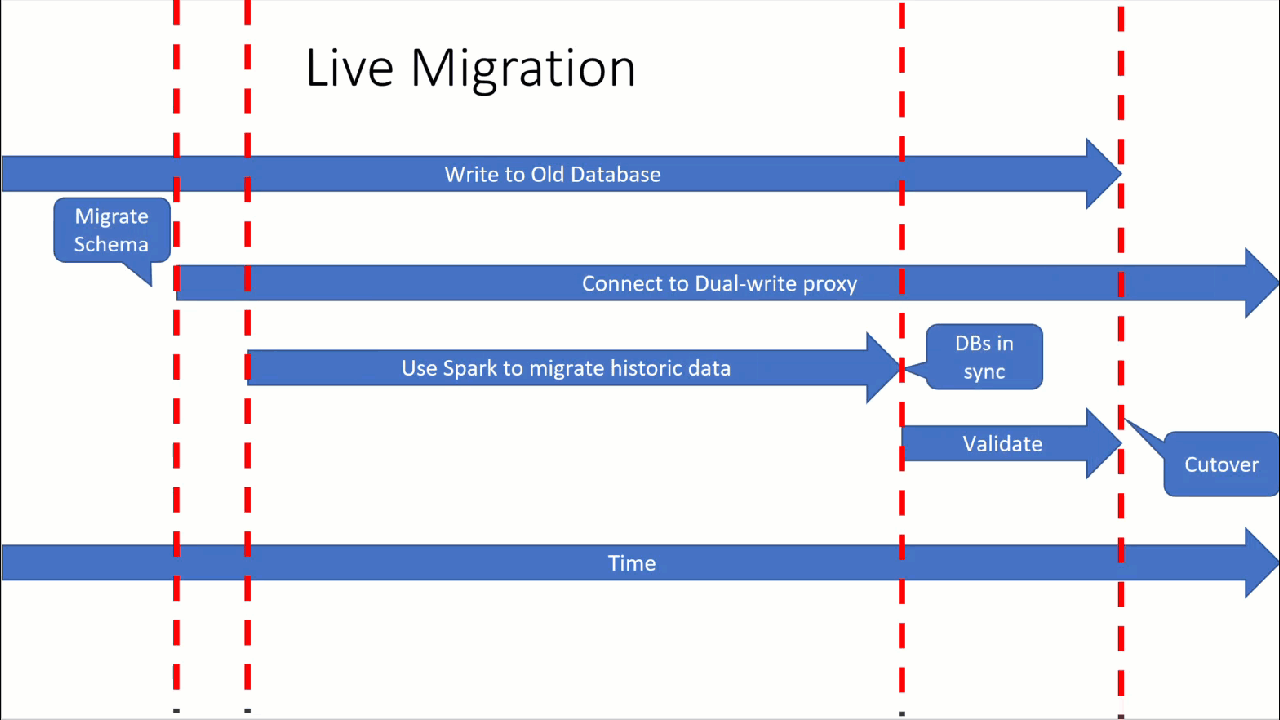
Prerequisites
-
Provision an Azure Managed Instance for Apache Cassandra cluster by using the Azure portal or the Azure CLI. Ensure that you can connect to your cluster with CQLSH.
-
Provision an Azure Databricks account inside your Managed Cassandra virtual network. Ensure that the account has network access to your source Cassandra cluster. We'll create a Spark cluster in this account for the historical data load.
-
Ensure that you've already migrated the keyspace/table scheme from your source Cassandra database to your target Cassandra managed-instance database.
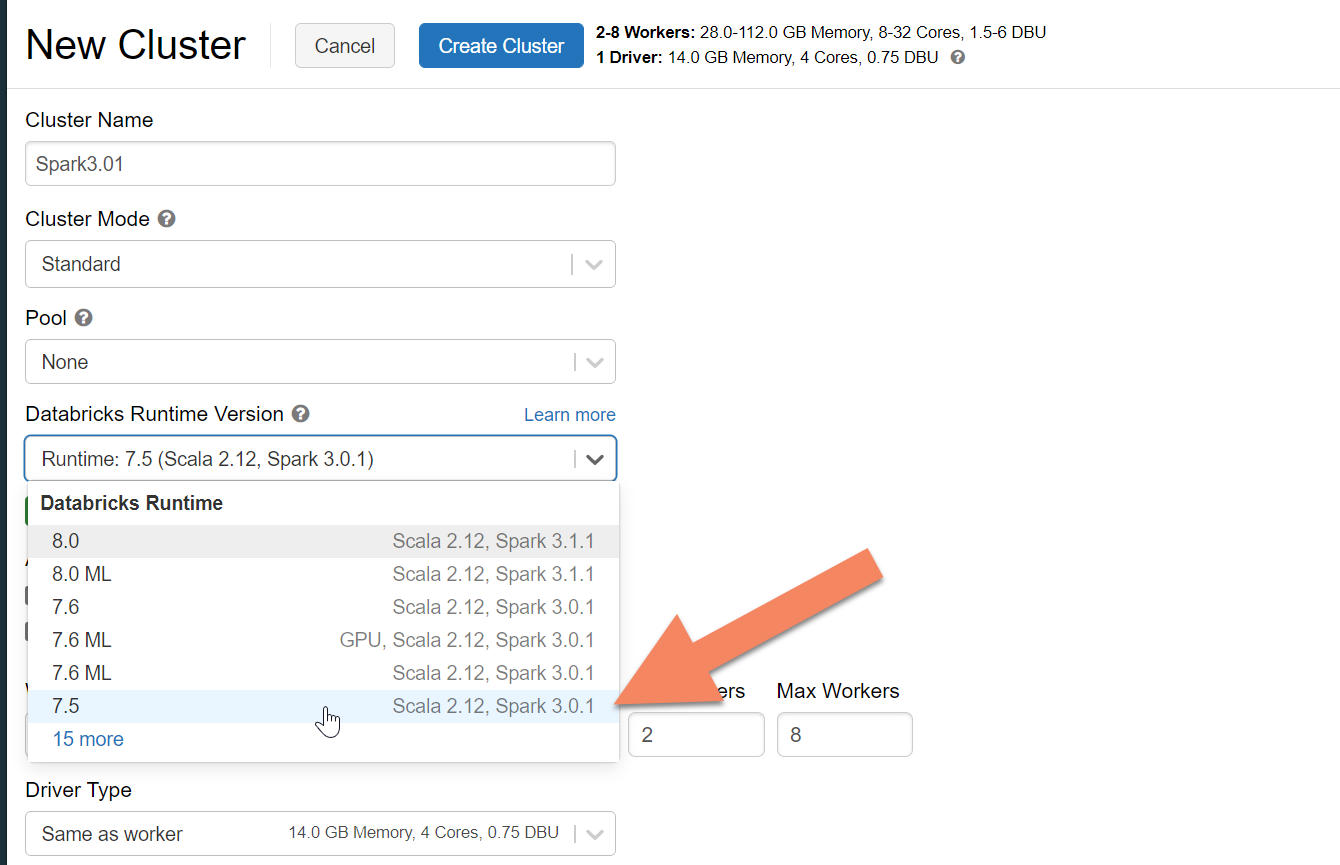
Provision a Spark cluster
We recommend selecting Azure Databricks runtime version 7.5, which supports Spark 3.0.
Add Spark dependencies
You need to add the Apache Spark Cassandra Connector library to your cluster to connect to any wire protocol compatible Apache Cassandra endpoints. In your cluster, select Libraries > Install New > Maven, and then add com.datastax.spark:spark-cassandra-connector-assembly_2.12:3.0.0 in Maven coordinates.
Important
If you have a requirement to preserve Apache Cassandra writetime for each row during the migration, we recommend using this sample. The dependency jar in this sample also contains the Spark connector, so you should install this instead of the connector assembly above. This sample is also useful if you want to perform a row comparison validation between source and target after historic data load is complete. See sections "run the historical data load" and "validate the source and target" below for more details.
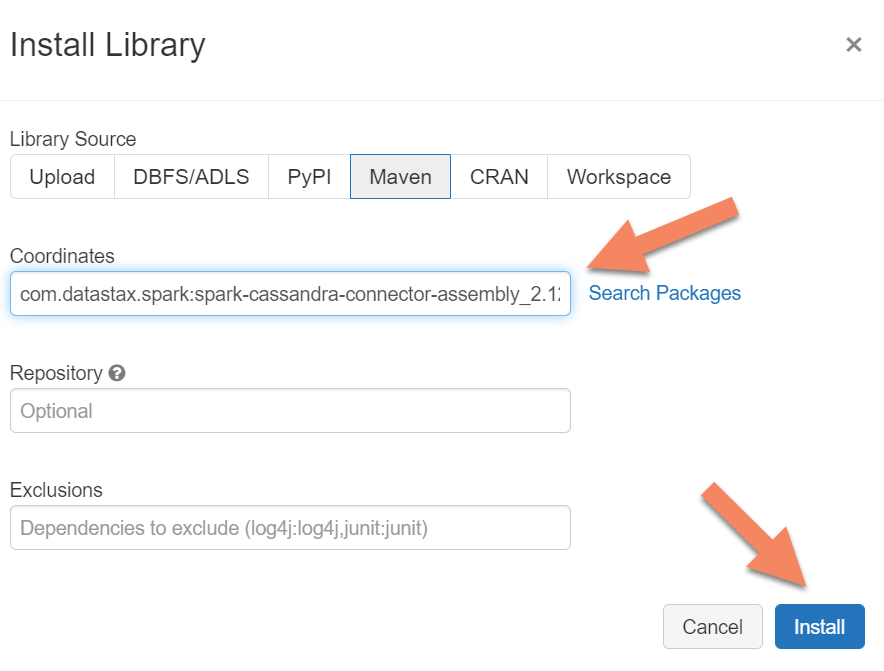
Select Install, and then restart the cluster when installation is complete.
Note
Be sure to restart the Azure Databricks cluster after the Cassandra Connector library is installed.
Install the dual-write proxy
For optimal performance during dual writes, we recommend installing the proxy on all nodes in your source Cassandra cluster.
#assuming you do not have git already installed sudo apt-get install git #assuming you do not have maven already installed sudo apt install maven #clone repo for dual-write proxy git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/cassandra-proxy.git #change directory cd cassandra-proxy #compile the proxy mvn package
Start the dual-write proxy
We recommend that you install the proxy on all nodes in your source Cassandra cluster. At minimum, run the following command to start the proxy on each node. Replace <target-server> with an IP or server address from one of the nodes in the target cluster. Replace <path to JKS file> with path to a local .jks file, and replace <keystore password> with the corresponding password.
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar localhost <target-server> --proxy-jks-file <path to JKS file> --proxy-jks-password <keystore password>
Starting the proxy in this way assumes that the following are true:
- Source and target endpoints have the same username and password.
- Source and target endpoints implement Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
If your source and target endpoints can't meet these criteria, read on for further configuration options.
Configure SSL
For SSL, you can either implement an existing keystore (for example, the one that your source cluster uses) or create a self-signed certificate by using keytool:
keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -alias selfsigned -keystore keystore.jks -storepass password -validity 360 -keysize 2048
You can also disable SSL for source or target endpoints if they don't implement SSL. Use the --disable-source-tls or --disable-target-tls flags:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar localhost <target-server> --source-port 9042 --target-port 10350 --proxy-jks-file <path to JKS file> --proxy-jks-password <keystore password> --target-username <username> --target-password <password> --disable-source-tls true --disable-target-tls true
Note
Make sure your client application uses the same keystore and password as the ones used for the dual-write proxy when you're building SSL connections to the database via the proxy.
Configure the credentials and port
By default, the source credentials will be passed through from your client app. The proxy will use the credentials for making connections to the source and target clusters. As mentioned earlier, this process assumes that the source and target credentials are the same. If necessary, you can specify a different username and password for the target Cassandra endpoint separately when starting the proxy:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar localhost <target-server> --proxy-jks-file <path to JKS file> --proxy-jks-password <keystore password> --target-username <username> --target-password <password>
The default source and target ports, when not specified, will be 9042. If either the target or the source Cassandra endpoint runs on a different port, you can use --source-port or --target-port to specify a different port number:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar localhost <target-server> --source-port 9042 --target-port 10350 --proxy-jks-file <path to JKS file> --proxy-jks-password <keystore password> --target-username <username> --target-password <password>
Deploy the proxy remotely
There might be circumstances in which you don't want to install the proxy on the cluster nodes themselves, and you prefer to install it on a separate machine. In that scenario, you need to specify the IP address of <source-server>:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar <source-server> <destination-server>
Warning
Installing and running the proxy remotely on a separate machine (rather than running it on all nodes in your source Apache Cassandra cluster) will impact performance while the live migration occurs. While it will work functionally, the client driver won't be able to open connections to all nodes within the cluster, and will rely on the single co-ordinator node (where the proxy is installed) to make connections.
Allow zero application code changes
By default, the proxy listens on port 29042. The application code must be changed to point to this port. However, you can change the port that the proxy listens on. You might do this if you want to eliminate application-level code changes by:
- Having the source Cassandra server run on a different port.
- Having the proxy run on the standard Cassandra port 9042.
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar source-server destination-server --proxy-port 9042
Note
Installing the proxy on cluster nodes does not require restart of the nodes. However, if you have many application clients and prefer to have the proxy running on the standard Cassandra port 9042 in order to eliminate any application-level code changes, you need to change the Apache Cassandra default port. You then need to restart the nodes in your cluster, and configure the source port to be the new port that you defined for your source Cassandra cluster.
In the following example, we change the source Cassandra cluster to run on port 3074, and we start the cluster on port 9042:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar source-server destination-server --proxy-port 9042 --source-port 3074
Force protocols
The proxy has functionality to force protocols, which might be necessary if the source endpoint is more advanced than the target or is otherwise unsupported. In that case, you can specify --protocol-version and --cql-version to force the protocol to comply with the target:
java -jar target/cassandra-proxy-1.0-SNAPSHOT-fat.jar source-server destination-server --protocol-version 4 --cql-version 3.11
After the dual-write proxy is running, you'll need to change the port on your application client and restart. (Or change the Cassandra port and restart the cluster if you've chosen that approach.) The proxy will then start forwarding writes to the target endpoint. You can learn about monitoring and metrics available in the proxy tool.
Run the historical data load
To load the data, create a Scala notebook in your Azure Databricks account. Replace your source and target Cassandra configurations with the corresponding credentials, and replace the source and target keyspaces and tables. Add more variables for each table as required to the following sample, and then run. After your application starts sending requests to the dual-write proxy, you're ready to migrate historical data.
import com.datastax.spark.connector._
import com.datastax.spark.connector.cql._
import org.apache.spark.SparkContext
// source cassandra configs
val sourceCassandra = Map(
"spark.cassandra.connection.host" -> "<Source Cassandra Host>",
"spark.cassandra.connection.port" -> "9042",
"spark.cassandra.auth.username" -> "<USERNAME>",
"spark.cassandra.auth.password" -> "<PASSWORD>",
"spark.cassandra.connection.ssl.enabled" -> "true",
"keyspace" -> "<KEYSPACE>",
"table" -> "<TABLE>"
)
//target cassandra configs
val targetCassandra = Map(
"spark.cassandra.connection.host" -> "<Source Cassandra Host>",
"spark.cassandra.connection.port" -> "9042",
"spark.cassandra.auth.username" -> "<USERNAME>",
"spark.cassandra.auth.password" -> "<PASSWORD>",
"spark.cassandra.connection.ssl.enabled" -> "true",
"keyspace" -> "<KEYSPACE>",
"table" -> "<TABLE>",
//throughput related settings below - tweak these depending on data volumes.
"spark.cassandra.output.batch.size.rows"-> "1",
"spark.cassandra.output.concurrent.writes" -> "1000",
"spark.cassandra.connection.remoteConnectionsPerExecutor" -> "1",
"spark.cassandra.concurrent.reads" -> "512",
"spark.cassandra.output.batch.grouping.buffer.size" -> "1000",
"spark.cassandra.connection.keep_alive_ms" -> "600000000"
)
//set timestamp to ensure it is before read job starts
val timestamp: Long = System.currentTimeMillis / 1000
//Read from source Cassandra
val DFfromSourceCassandra = sqlContext
.read
.format("org.apache.spark.sql.cassandra")
.options(sourceCassandra)
.load
//Write to target Cassandra
DFfromSourceCassandra
.write
.format("org.apache.spark.sql.cassandra")
.options(targetCassandra)
.option("writetime", timestamp)
.mode(SaveMode.Append)
.save
Note
In the preceding Scala sample, you'll notice that timestamp is being set to the current time before reading all the data in the source table. Then, writetime is being set to this backdated time stamp. This ensures that records that are written from the historical data load to the target endpoint can't overwrite updates that come in with a later time stamp from the dual-write proxy while historical data is being read.
Important
If you need to preserve exact time stamps for any reason, you should take a historical data migration approach that preserves time stamps, such as this sample. The dependency jar in the sample also contains the Spark connector, so you do not need to install the Spark connector assembly mentioned in the earlier pre-requisites - having both installed in your Spark cluster will cause conflicts.
After the historical data load is complete, your databases should be in sync and ready for cutover. However, we recommend that you validate the source and target to ensure they match before finally cutting over.
Note
If you used the cassandra migrator sample mentioned above for preserving writetime, this includes the capability to validate the migration by comparing rows in source and target based on certain tolerances.